Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH)
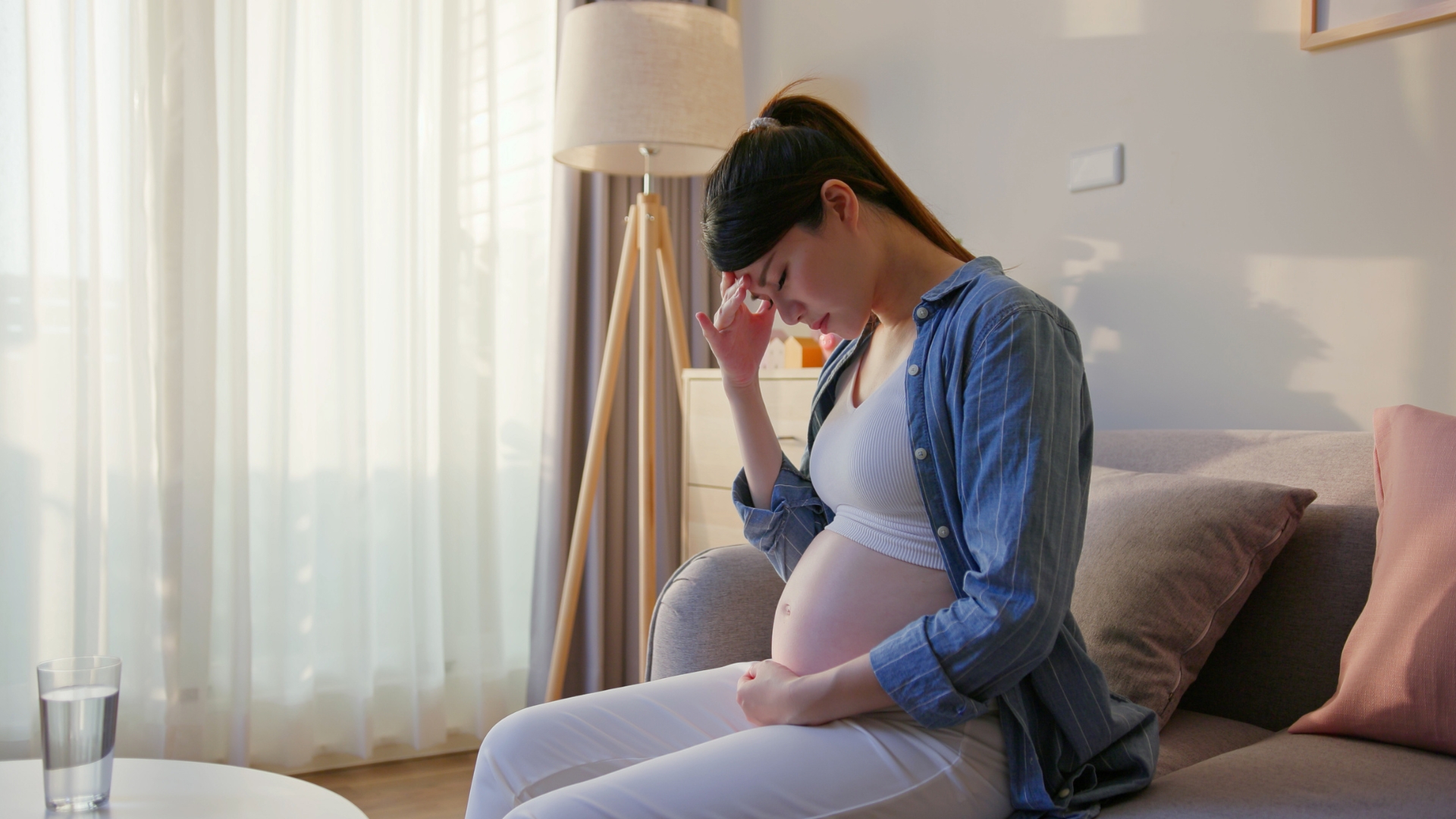

Pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is a condition that occurs during pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure. It can occur in both normal and high-risk pregnancies and can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the baby if left untreated.
Symptoms of PIH may include headache, swelling in the face, hands, and feet, and visual disturbances. PIH is diagnosed if the blood pressure is higher than 140/90 mm Hg after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Here are several factors that can increase the risk of PIH, including:
- Age: Women over the age of 35 are at an increased risk of PIH.
- Previous PIH: Women who have had PIH in a previous pregnancy are at an increased risk of developing it again.
- Obesity: Obesity can increase the risk of PIH.
- Family history: Women with a family history of hypertension are at an increased risk of PIH.
PIH can be managed through medication and close monitoring by a healthcare provider. It is important for pregnant women to receive regular prenatal care to monitor for PIH and other complications.
Here are some frequently asked questions about PIH:
What are the symptoms of PIH?
How is PIH diagnosed?
How is PIH treated?
What are the risks of PIH for the mother and the baby?
Can PIH be prevented?