Gestational Diabetes
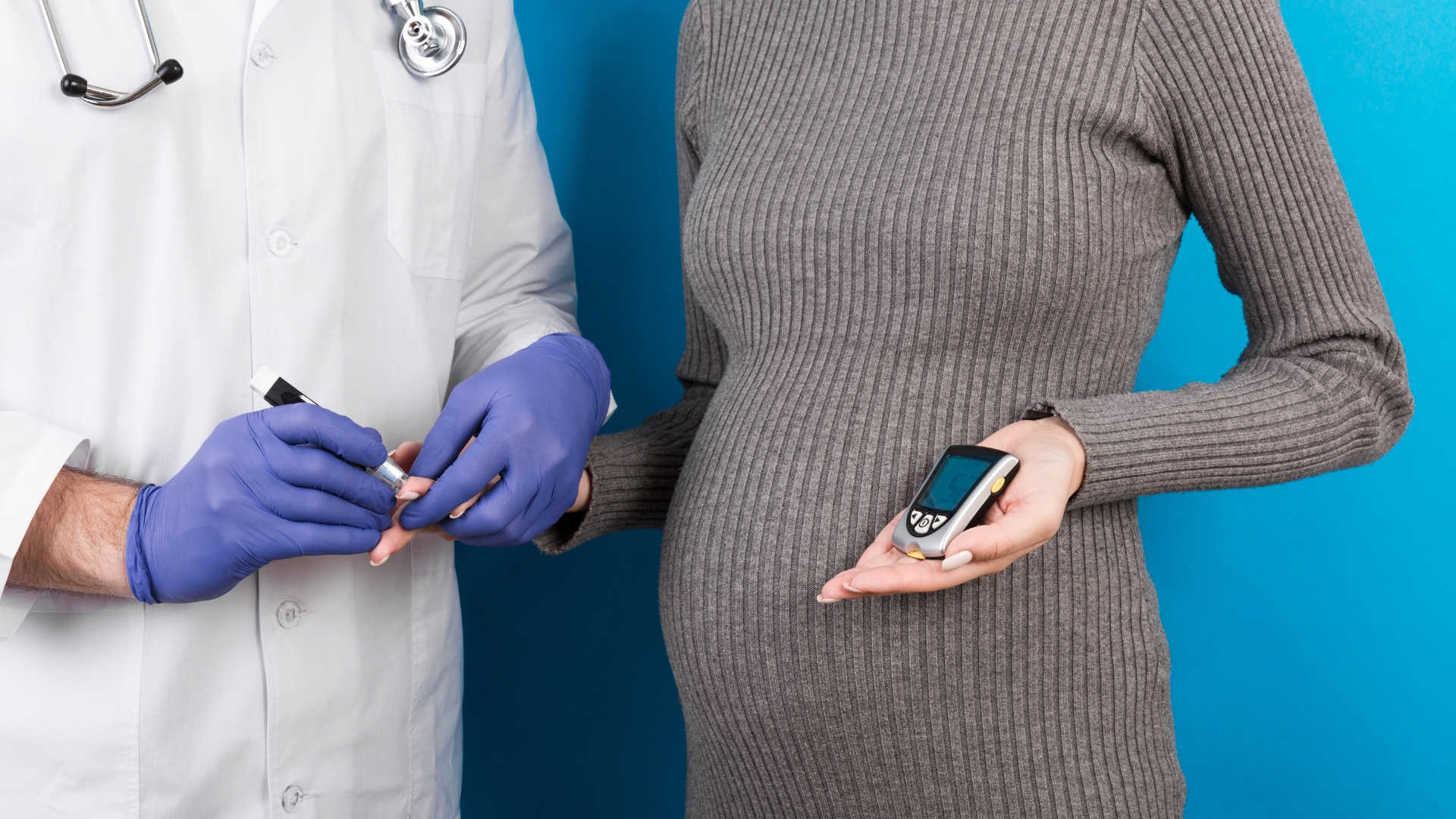

Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. It is caused by the hormonal changes of pregnancy, which can interfere with the action of insulin, a hormone that helps regulate the level of sugar in the blood. Gestational diabetes can develop in any pregnancy, but it is more common in women who are overweight or obese, have a family history of diabetes, or have had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy.
The main symptom of gestational diabetes is high blood sugar, which can be detected during routine prenatal blood tests. If left untreated, gestational diabetes can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby, such as high blood pressure, preterm delivery, and an increased risk of cesarean delivery.
Gestational diabetes can be managed with a combination of diet, exercise, and possibly insulin injections. Close monitoring of blood sugar levels is important to ensure the health of the mother and the baby. After delivery, most women with gestational diabetes will no longer have diabetes, but they are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. To reduce this risk, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and to continue regular medical checkups.
If you have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes, here are some steps you can take to manage your condition and maintain the health of you and your baby:
- Follow a healthy diet: Your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help you plan a healthy diet that includes a variety of foods and helps you maintain good blood sugar control. This may include eating regular meals and snacks, avoiding foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats, and choosing foods that are high in fiber and nutrients.
- Get regular exercise: Exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve your overall health. Talk to your healthcare provider about what types of exercise are safe for you during pregnancy.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels: You may need to check your blood sugar levels at home using a blood glucose meter. Your healthcare provider will tell you how often to check your blood sugar and what your target range should be.
- Take medications as prescribed: If diet and exercise alone are not enough to control your blood sugar, your healthcare provider may prescribe insulin injections or other medications to help manage your condition. It is important to take these medications as directed and to follow up with your healthcare provider regularly.
- Attend all prenatal visits: Regular prenatal visits are important for monitoring your health and the health of your baby. Be sure to attend all of your appointments and report any concerns or symptoms to your healthcare provider.
- Stay healthy: In addition to managing your gestational diabetes, it is important to practice good self-care during pregnancy. This includes getting enough rest, staying hydrated, and avoiding tobacco and alcohol use.