Egg freezing
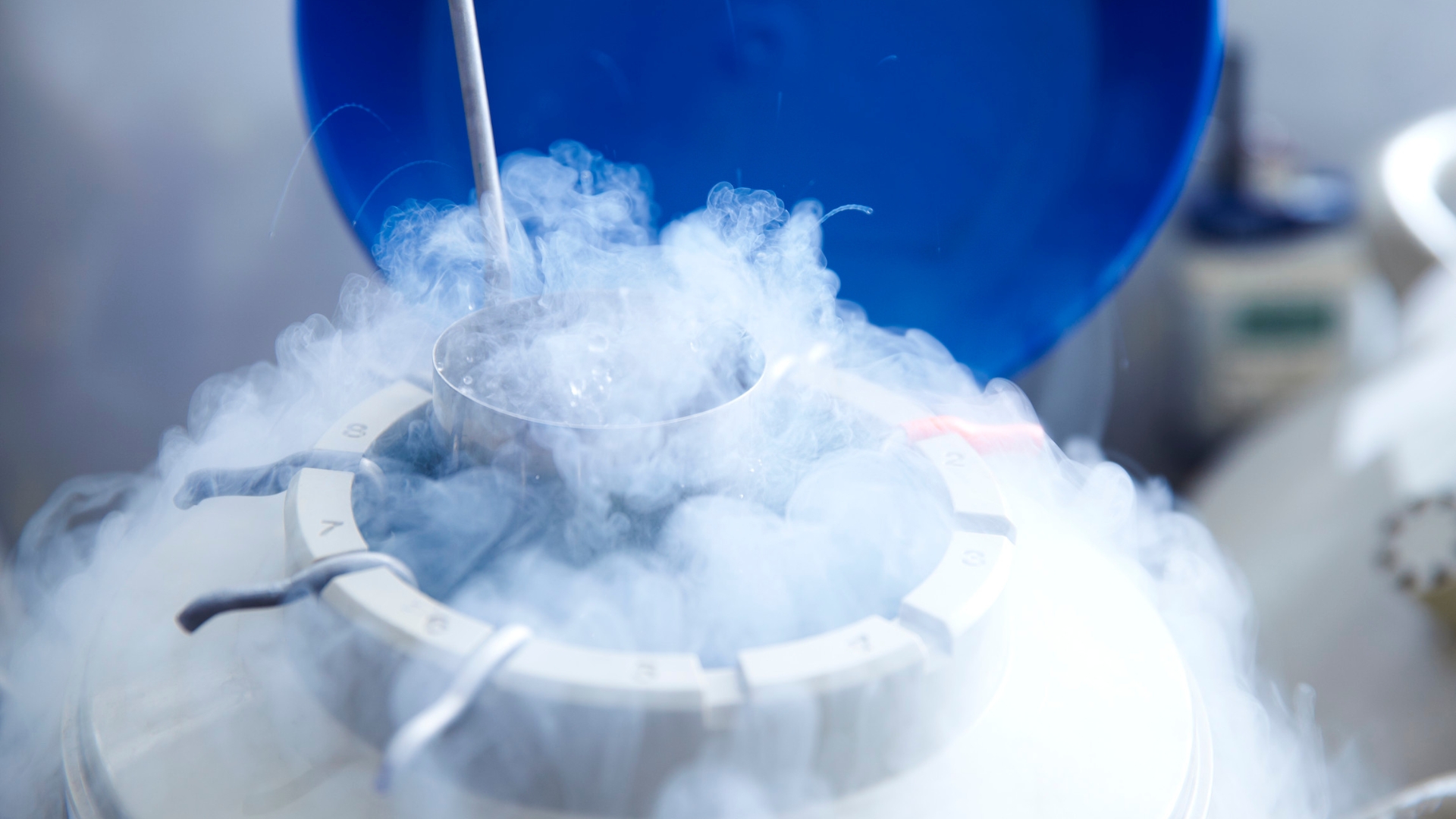

Egg freezing, also known as oocyte cryopreservation, is a fertility preservation method that allows women to have their eggs (oocytes) extracted and frozen for later use. This can be done for a variety of reasons, such as preserving fertility before undergoing cancer treatment, or for women who wish to delay childbearing for personal or professional reasons.
The process of egg freezing involves several steps:
- Ovarian stimulation:To increase the number of eggs that can be collected, women are given fertility medications that stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
- Egg retrieval: The eggs are then removed from the ovaries through a minor surgical procedure called transvaginal ultrasound-guided egg retrieval.
- Egg freezing: The eggs are then frozen using a process called vitrification, which involves rapidly cooling the eggs to ultra-low temperatures (-196°C) in order to turn them into a glass-like state.
- Thawing and fertilization: When the woman is ready to use the frozen eggs, they are thawed and fertilized using in vitro fertilization (IVF) techniques. If the fertilized eggs develop into embryos, they can be transferred to the woman's uterus in the hopes of achieving pregnancy.
Egg freezing is generally considered safe, but it is not without risks. Some women may experience side effects from the fertility medications used in the process, and there is a small risk of bleeding or infection associated with the egg retrieval procedure. There is also no guarantee that the frozen eggs will be viable when thawed, or that a pregnancy will result from the use of frozen eggs.